Planar CT Flying Shot Imaging Technology
Planar CT Flying Shot Imaging Technology consists of two core components: high-speed flying shot and real-time reconstruction. Using this technology, inspection speed is increased by more than 4.5 times compared to the previous generation models. High-speed flying shot primarily utilizes high-speed motion control and flying shot imaging. While ensuring high-speed equipment movement, it can algorithmically correct inherent mechanical deviations and assembly deviations using high-precision calibration technology according to reconstruction requirements. Planar CT real-time reconstruction technology performs the reconstruction of X-Ray projection images concurrently with the flying shot process, eliminating the need to wait for all projection images to be acquired before reconstruction. In other words, upon completion of the flying shot, 3D/CT reconstruction can be completed simultaneously.
Parallel-Plane Flying Shot Imaging Technology mainly offers the following advantages:
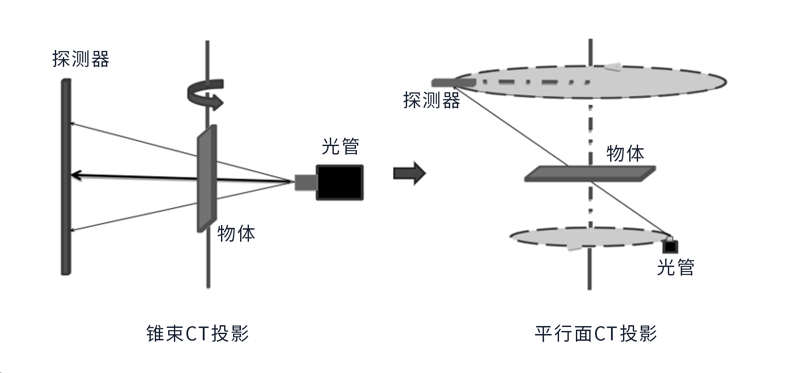
Schematic diagram of Cone-Beam CT projection and Parallel-Plane CT projection
Parallel-Plane Flying Shot Imaging Technology mainly consists of two parts: Parallel-Plane CT Projection Technology and Flying Shot Imaging Reconstruction Technology. It balances application scenarios, inspection accuracy, and inspection efficiency, effectively addressing the main issues in current X-Ray inspection across various fields.
A. Parallel-Plane CT Projection Technology
Parallel-Plane CT Projection Technology, in contrast to Cone-Beam CT Projection Technology, refers to the dual-ring motion of the X-Ray source and detector around the central axis, with the object being reconstructed on this central axis.
B. Flying Shot Reconstruction Technology
Flying Shot Reconstruction Technology, also known as Real-Time Reconstruction Technology, refers to the technology that completes rapid imaging and real-time reconstruction while the inspected object is in high-speed motion. As shown in the timing analysis below, Flying Shot Reconstruction Technology can significantly reduce reconstruction time compared to traditional reconstruction techniques, enabling parallel processing of imaging and reconstruction.
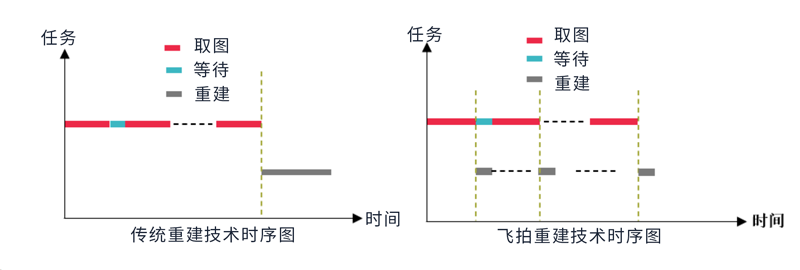
Timing diagram of Conventional and Flying Shot Reconstruction Technologies




